Simulation-based procedural training has emerged as a cornerstone in various fields, offering a safe and controlled environment for learners to hone their skills.
This training methodology, rooted in experiential learning, replicates real-world scenarios to provide hands-on practice without the risks associated with actual tasks.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the essence of simulation-based procedural training, its applications across diverse industries, key components, benefits, challenges, and the future landscape it envisions.
Understanding Simulation-Based Procedural Training
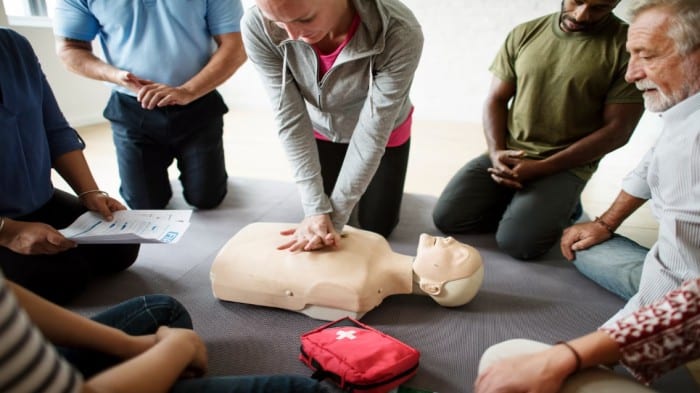 Simulation-based procedural training involves the use of simulated environments to replicate real-life scenarios, allowing learners to practice and refine specific skills or procedures.
Simulation-based procedural training involves the use of simulated environments to replicate real-life scenarios, allowing learners to practice and refine specific skills or procedures.
These simulations mimic the complexities of the actual task, providing an immersive experience that fosters experiential learning.
Whether it’s central line training focused on medical procedures, flight simulations, or emergency response training, the fundamental principle remains consistent: providing a safe yet realistic environment for skill acquisition and mastery.
Applications Across Industries
The versatility of simulation-based procedural training transcends industries, finding application in fields ranging from healthcare to aviation, military training, manufacturing, and beyond.
In healthcare, medical simulators allow practitioners to rehearse surgical procedures, patient care protocols, and learn different emergency medicine skills courses focused on interventions.
Flight simulators replicate cockpit environments, enabling pilots to practice various scenarios, from routine flights to emergency landings. Similarly, military simulations prepare soldiers for combat situations, enhancing their tactical proficiency and decision-making under pressure. In manufacturing, simulators facilitate training on equipment operation, safety protocols, and troubleshooting techniques, minimizing downtime and optimizing productivity.
Key Components of Simulation-Based Procedural Training
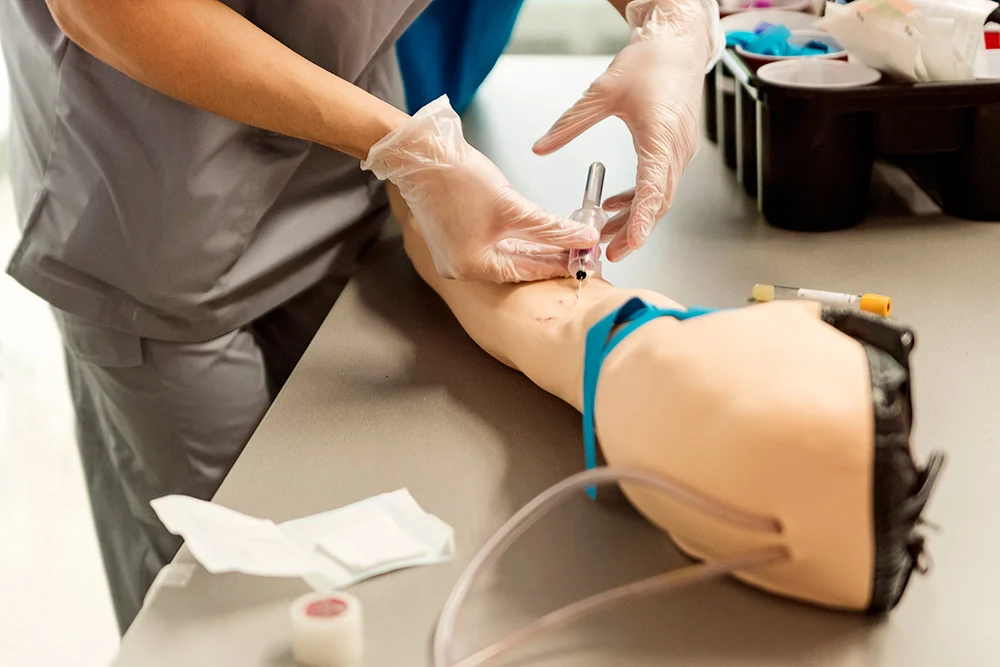
- Simulated Environment: Central to simulation-based training is the creation of a realistic environment that mirrors real-world scenarios. This environment may range from physical simulators to virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) platforms, depending on the training objectives and available resources.
- Task Representation: Simulations must accurately represent the tasks or procedures being trained. This includes replicating relevant equipment, tools, and environmental factors to ensure a high-fidelity learning experience.
- Feedback Mechanism: Effective feedback is crucial for learning and improvement. Simulation-based training often incorporates feedback mechanisms, such as performance metrics, instructor guidance, and debriefing sessions, to provide learners with actionable insights into their performance.
- Interactivity: Interactivity fosters engagement and skill retention. Simulations may include interactive elements that require learners to make decisions, solve problems, and respond to changing scenarios, promoting active participation and critical thinking.
- Scalability: Scalability is essential for accommodating varying skill levels and training needs. Simulation-based training programs should be adaptable to individual learning paces and proficiency levels, allowing for personalized learning experiences.
Benefits of Simulation-Based Procedural Training
- Safe Learning Environment: Simulation-based training offers a risk-free environment where learners can make mistakes without consequences, fostering experimentation and exploration.
- Skill Mastery: Through repeated practice in simulated scenarios, learners can master procedural skills more effectively, building confidence and competence over time.
- Cost-effectiveness: While initial investment in simulation technology may be significant, the long-term cost savings associated with reduced training-related errors, improved efficiency, and optimized resource utilization make simulation-based training a cost-effective solution.
- Enhanced Retention: The immersive nature of simulation-based training enhances knowledge retention by providing memorable learning experiences that resonate with learners long after the training concludes.
- Adaptability: Simulations can be tailored to address specific training objectives and accommodate diverse learning styles, making them suitable for learners with varying backgrounds and skill levels.
The Future of Simulation-Based Procedural Training
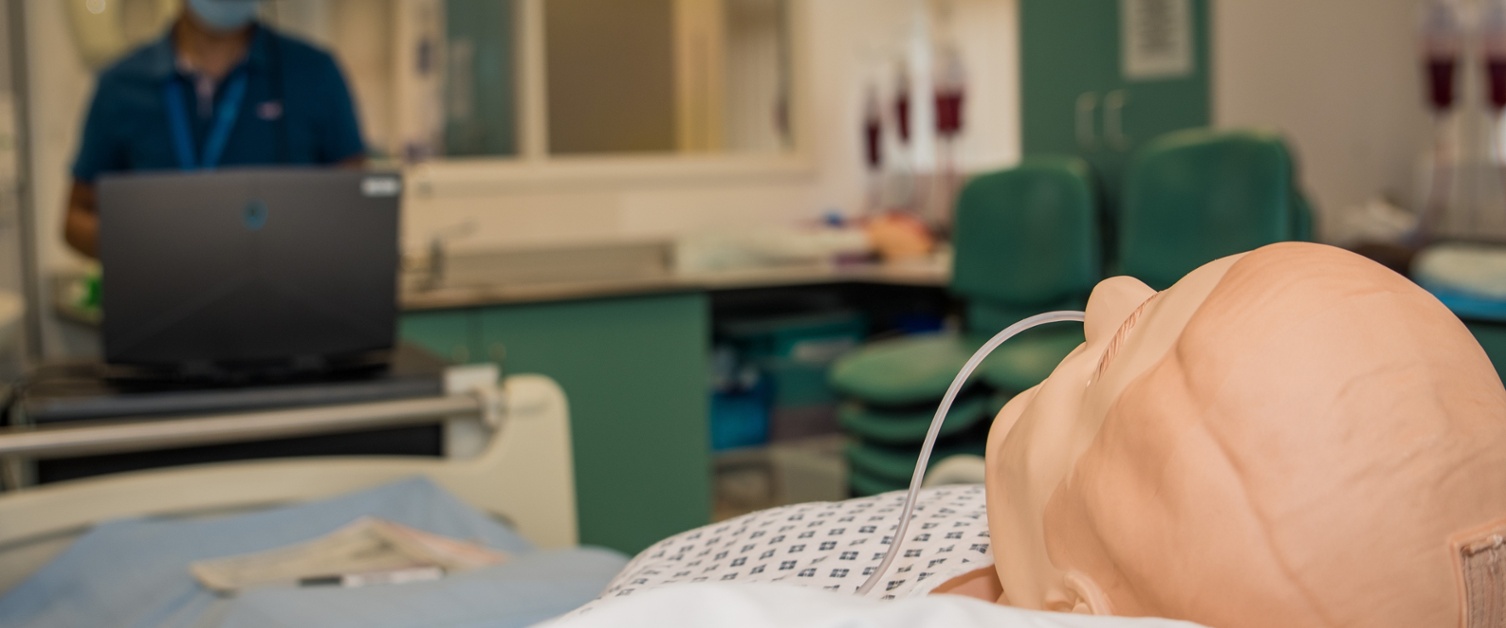 As technology continues to evolve, the future of simulation-based procedural training holds promise for even more immersive and effective learning experiences.
As technology continues to evolve, the future of simulation-based procedural training holds promise for even more immersive and effective learning experiences.
Advancements in virtual reality, augmented reality, artificial intelligence, and haptic feedback systems are poised to enhance the realism and interactivity of simulations, further blurring the line between virtual and real-world training environments.
Additionally, increased accessibility to simulation technology and growing emphasis on competency-based education are expected to drive broader adoption across industries, democratizing access to high-quality training experiences.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
In addition to the established benefits and challenges of simulation-based procedural training, several emerging trends and innovations are shaping the landscape of this educational approach.
From advancements in technology to novel methodologies, these developments hold the potential to further enhance the effectiveness and accessibility of simulation-based training.
Technological Advancements
The rapid evolution of technology, particularly in areas such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and artificial intelligence (AI), is driving significant advancements in simulation-based training. VR and AR technologies are becoming more immersive and realistic, offering learners an even more authentic experience that closely mirrors real-world scenarios.
AI algorithms are being integrated into simulations to provide adaptive feedback and personalized learning experiences, tailoring training programs to the individual needs and learning styles of each learner.
Mobile and Remote Training Solutions
The proliferation of mobile devices and high-speed internet connectivity has paved the way for mobile and remote simulation-based training solutions.
Learners can now access training modules and simulations from anywhere, at any time, using their smartphones, tablets, or laptops. This flexibility enables more convenient and accessible training options, particularly for professionals who may have limited time for traditional in-person training sessions.
Challenges and Considerations
- Technology Limitations: Simulation technology may have limitations in replicating certain aspects of real-world scenarios, potentially affecting the fidelity of the training experience.
- Resource Intensiveness: Developing and maintaining simulation-based training programs requires significant resources, including financial investment, specialized equipment, and skilled personnel.
- Integration with Curriculum: Integrating simulation-based training into existing educational or training curricula may pose challenges related to scheduling, logistics, and alignment with learning objectives.
- Learner Engagement: Maintaining learner engagement over extended simulation sessions can be challenging, especially if the simulations lack variety or fail to capture learners’ interest.
- Assessment Validity: Ensuring the validity and reliability of assessments within simulation-based training environments is essential for accurately measuring learners’ proficiency and progress.
Conclusion
Simulation-based procedural training stands at the forefront of modern education and skill development, offering a dynamic platform for experiential learning across diverse fields.
By providing a safe yet realistic environment for hands-on practice, simulation-based training equips learners with the skills and confidence needed to navigate real-world challenges effectively.
As technology advances and educational paradigms evolve, simulation-based training is poised to play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of learning and professional development.





